


Quito: Hydropower in the Pipes
Using the water system to power essential urban resilience
Status
City description
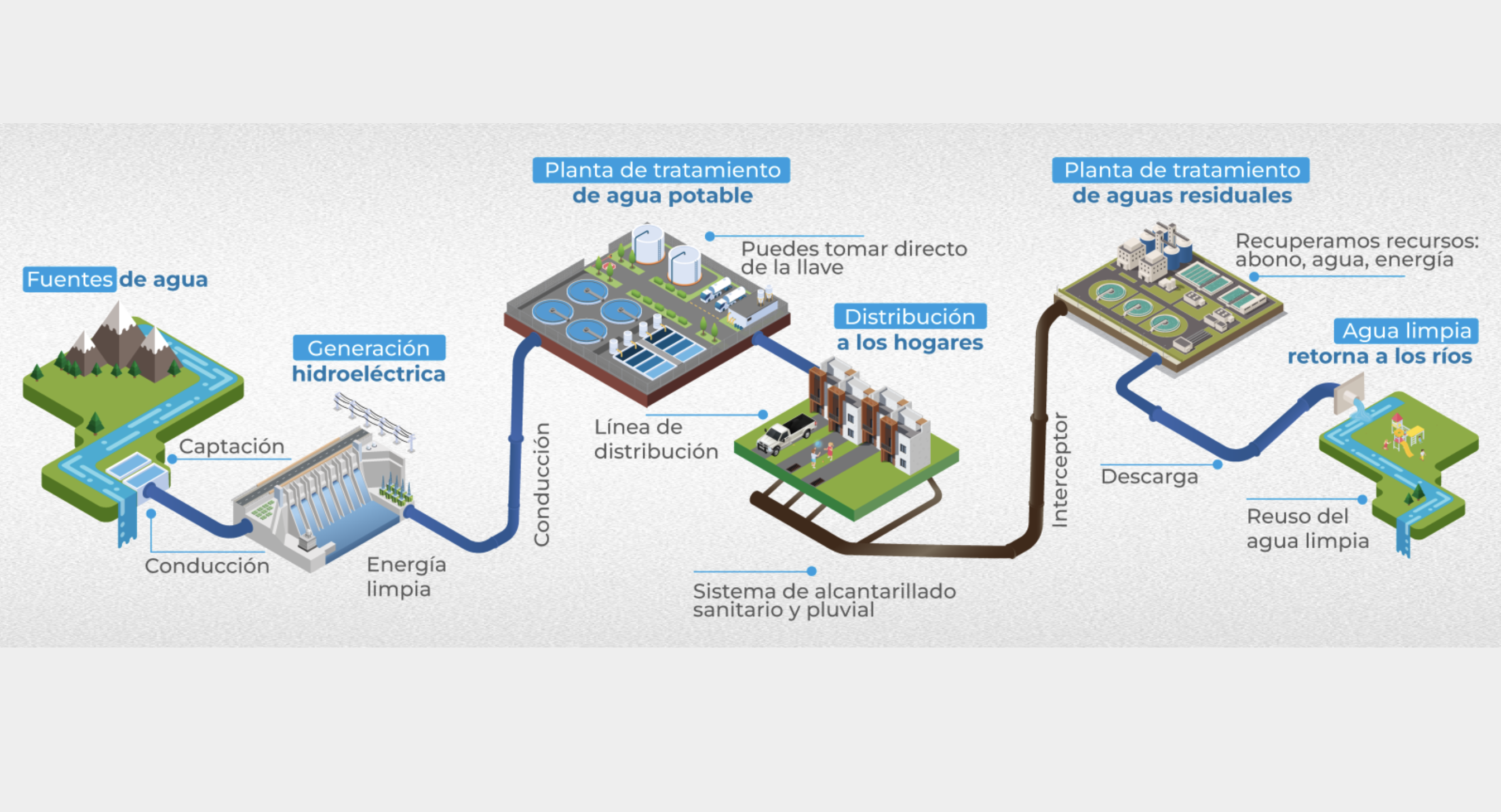
Quito, capital of Ecuador, is a high-altitude metropolitan area located at 2,850 metres in the Andes. The city spans 372 km² and is home to around 2.8-3 million people across its wider metropolitan area. Its steep terrain, seismic exposure, and dependence on electrically powered water systems create high vulnerability to energy disruptions. Ensuring uninterrupted water supply is therefore a core resilience priority.
Challenge
Quito’s water system requires continuous electricity for pumping and treatment. National blackouts and climate-related threats can interrupt water delivery, jeopardising health, safety, and economic functions.
Solution
EPMAPS developed a self-sufficient water-energy system by installing hydropower turbines in key sections of the water network. This allows the utility to generate clean, local electricity, reduce dependence on the grid, cut costs, and maintain operations even during major outages.
Key Impacts
80% of EPMAPS’ electricity demand
covered by in-network hydropower.
45% of city water demand protected
during the 2024 blackout via the Papallacta Integrated System.
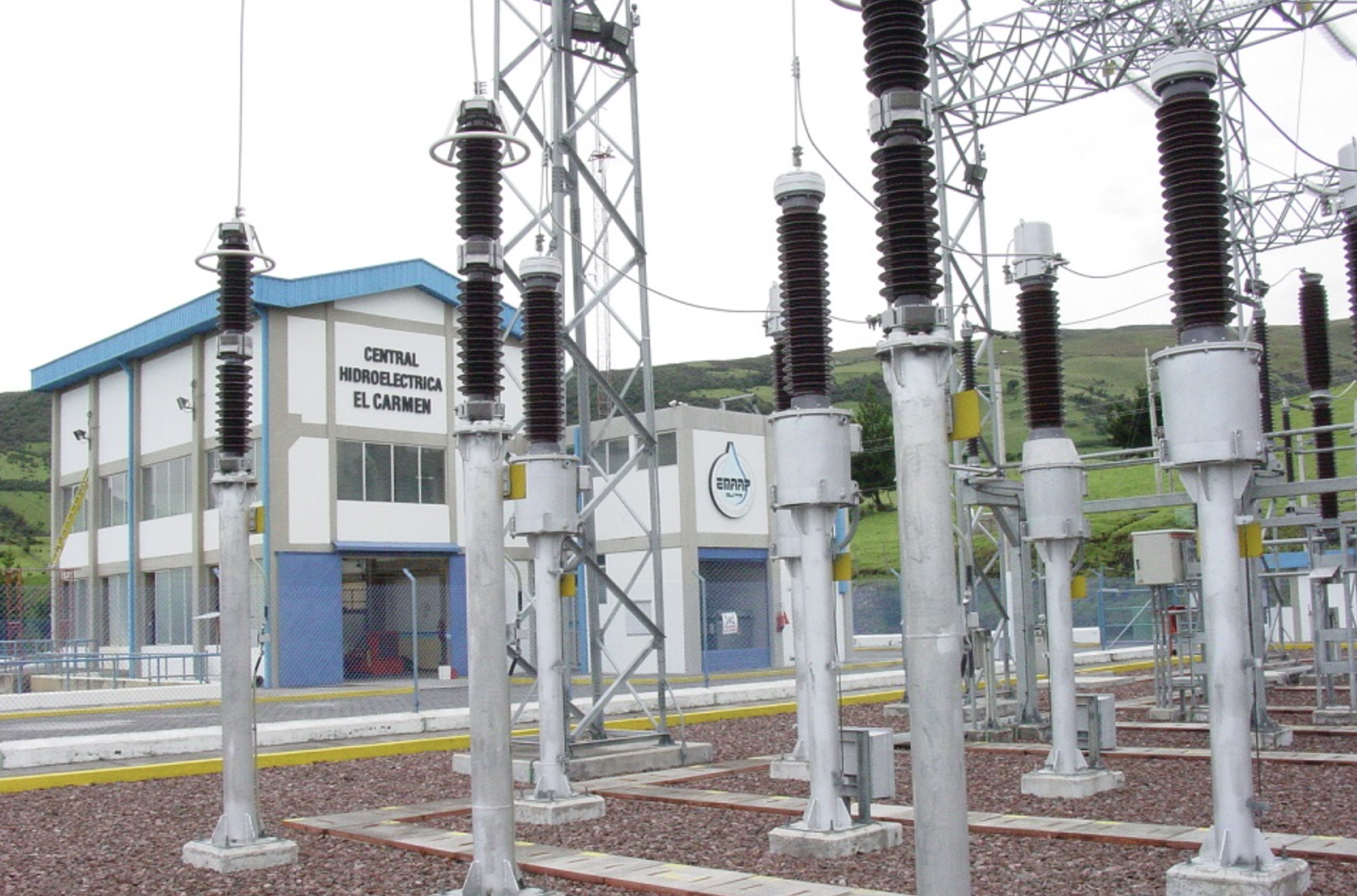
14.7 MW + 8.3 MW generated
by the Recuperadora and Carmen plants.
10-20% expected efficiency boost
from planned floating solar PV.
Reduced operational costs
and improved financial resilience.
Strengthened reliability
of essential water services for 3 million residents.


Comments ()